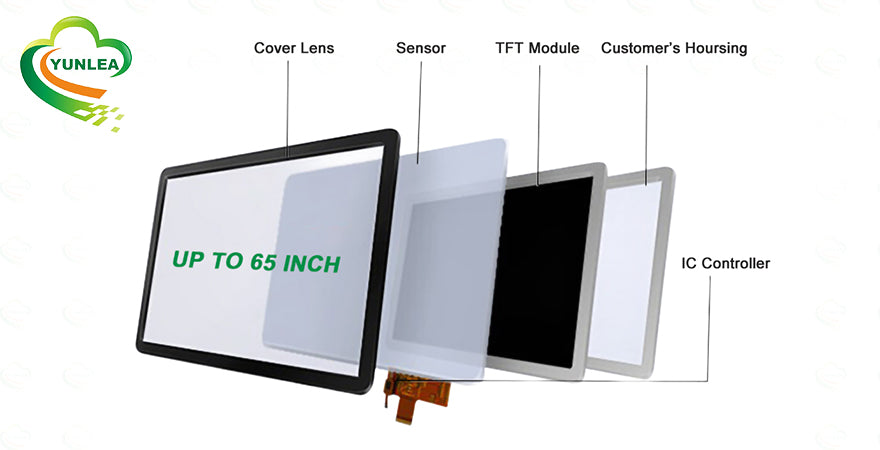
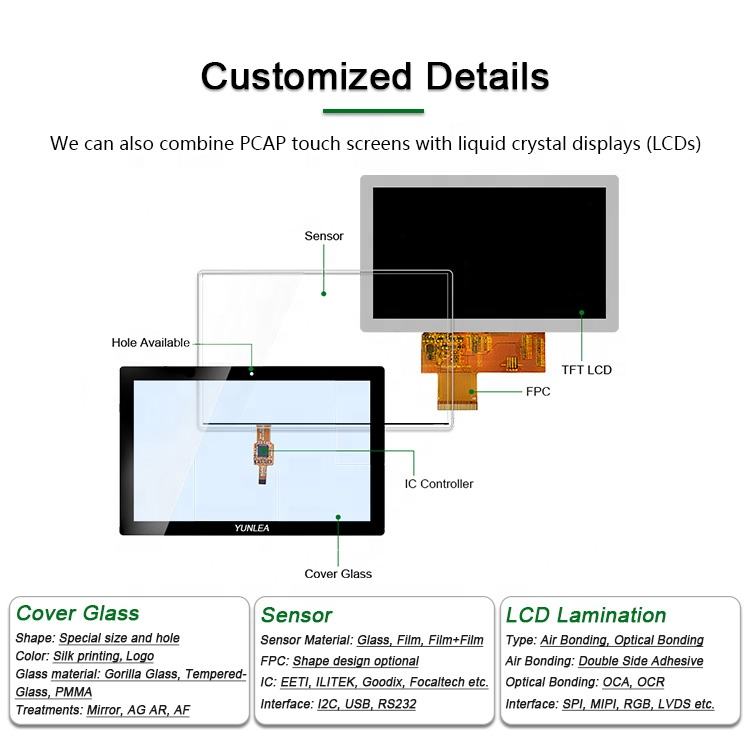
TFT LCD vs. OLED: Which Display Technology is Best for Your Needs?

At Yunlea, we specialize in touchscreen and display technologies, helping customers make informed decisions about the best display options for their products. Two of the most widely used technologies today are TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes). Here’s an in-depth comparison of how these technologies work, their strengths, and where each one excels.
TFT LCD Technology: How It Works
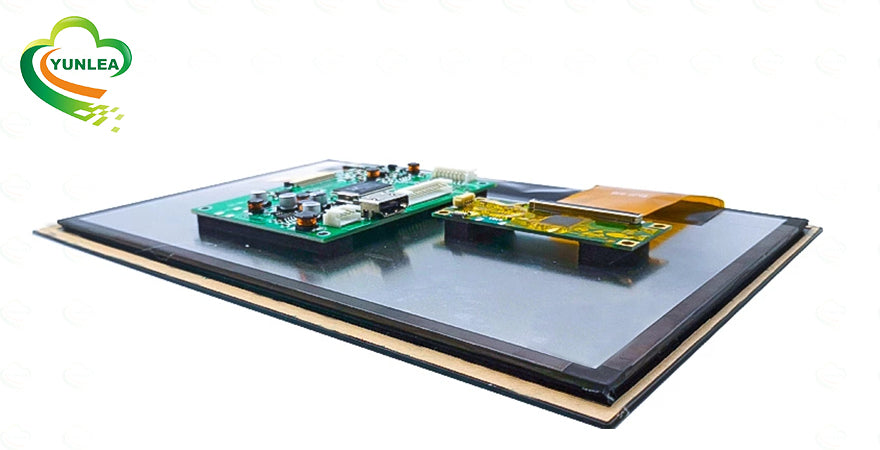
TFT LCDs operate by using thin-film transistors to control liquid crystals, which modulate light from a backlight (typically LEDs) to display images. The liquid crystals themselves do not emit light, so a backlight is essential to create the visible display.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective: TFT LCDs are less expensive to manufacture, making them ideal for cost-conscious applications.
- High Brightness: They perform well even under bright sunlight, maintaining high levels of visibility.
- No Burn-In: Unlike OLEDs, TFT LCDs do not suffer from burn-in, where static images leave lasting imprints on the screen.
Limitations:
- Limited Viewing Angles: TFT LCDs tend to lose color accuracy and contrast when viewed from side angles.
- Black Levels: Because of the constant backlight, achieving deep blacks is difficult, leading to lower contrast in darker scenes.
OLED Technology: How It Works
OLED displays are made up of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through them. Unlike TFT LCDs, OLED displays do not need a backlight, as each pixel produces its own light, allowing for excellent contrast and true black levels.
Advantages:
- Superior Contrast and Colors: OLEDs can turn individual pixels off, resulting in true blacks and stunning contrast.
- Wider Viewing Angles: OLED displays maintain consistent color and brightness, regardless of the viewing angle.
- Flexible Design: OLED's organic material can be used in flexible and curved displays, enabling innovative designs.
Limitations:
- Higher Cost: The production of OLED displays is more expensive, often reflected in the final product's price.
- Burn-In Risk: OLEDs can suffer from burn-in, where static images may leave permanent marks on the screen after prolonged display.
Conclusion
Both TFT LCD and OLED offer unique benefits, and the right choice depends on your specific product requirements. For budget-friendly and durable displays, TFT LCD is a reliable option. However, if superior image quality and viewing experience are your priorities, OLED is the clear winner. At Yunlea, we offer both TFT LCD and OLED solutions tailored to various industries, ensuring you get the perfect display for your application.